Have you ever wondered what gives some Asian dishes their distinctive tangy flavor?
Finding the perfect balance of flavors in Asian cuisine can be challenging, especially when exploring less familiar ingredients.
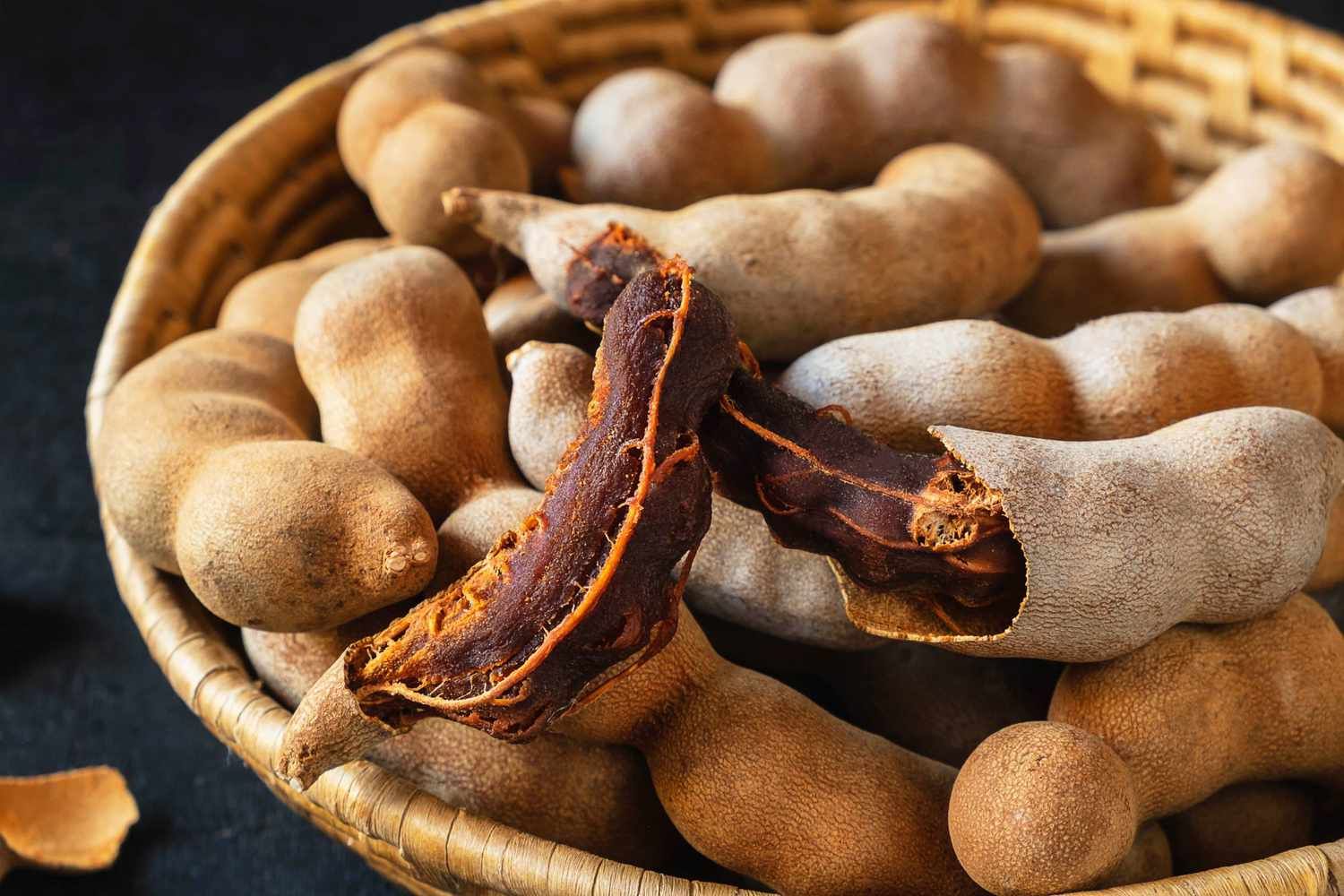
Tamarind is a versatile ingredient widely used across Asia in sauces, soups, marinades, and even beverages, offering a unique sour taste that enhances the dish’s flavor profile.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the various roles tamarind plays in Asian cuisine, its historical significance, health benefits, different varieties, and how you can experience these flavors on a culinary tour.
The Versatile Uses of Tamarind in Asian Cuisine

Tamarind is celebrated for its ability to introduce a sweet and sour flavor that is essential in many Asian dishes. This versatile fruit is used in a variety of forms such as paste, pulp, and dried powder, making it a staple in the kitchen for creating depth in flavor profiles. From tamarind asian cuisine like Thai to Indian, its presence is notable in numerous traditional dishes.
Among its many applications, tamarind excels in:
- Sauces: It’s often a key ingredient in sweet and sour sauces, providing a tangy base that complements both meat and vegetables.
- Marinades: Tamarind helps tenderize meat while infusing it with flavor, making it perfect for barbecue and grilled dishes.
- Beverages: Refreshing drinks like tamarind water or agua de tamarindo highlight its versatility beyond solid foods, offering a tart refreshment option.
Tamarind’s adaptability extends to various culinary creations, enhancing not just the main dishes but also elevating the flavors of sides and drinks. Whether it’s the tangy kick in a pad Thai or the subtle tartness in a marinade, tamarind proves to be an indispensable part of tamarind asian cuisine. Its ability to blend with other ingredients while maintaining its distinct taste is what makes it a beloved choice in kitchens across Asia.
Historical Significance of Tamarind in Asian Cooking

Tamarind has a storied past that intertwines deeply with Asian culinary traditions. Originally from Africa, it spread to Asia where it became heavily integrated into the local cuisines. The name ‘tamarind’ itself is derived from the Arabic term ‘tamar hind’, meaning ‘Indian date’, highlighting its profound connection to the region. Over the centuries, tamarind has been more than just a food ingredient; it has played a significant role in cultural rituals and traditional cooking methods across Asia, especially in India and Thailand.
In historical context, tamarind was not only valued for its unique flavor but also for its preservative qualities, which were essential before modern refrigeration. Its integration into Asian cooking includes a variety of uses:
- Sauces and chutneys: Tamarind adds a tangy depth to condiments.
- Traditional medicine: It has been used to treat everything from digestion issues to inflammation.
- Culinary rituals: Tamarind is integral in religious and festive cooking, symbolizing flavor and vitality. This deep-rooted historical significance makes tamarind a revered and essential ingredient in Asian kitchens, transcending mere taste to embody a rich cultural heritage.
Health Benefits of Tamarind in Your Diet

Tamarind isn’t just a flavor enhancer; it’s also packed with health benefits that make it a valuable addition to your diet. Rich in antioxidants, tamarind helps combat oxidative stress caused by free radicals, which are harmful molecules that can damage cells and lead to chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Additionally, tamarind is known for its digestive properties, aiding in efficient digestion and helping to relieve constipation due to its high fiber content. These benefits show why tamarind is more than just a tasty ingredient but a healthful one too.
Beyond its immediate nutritional benefits, tamarind has been utilized in traditional medicine across Asia for centuries. It is often used to treat a range of ailments from inflammation to stomach discomfort. This traditional use underscores tamarind’s role as a natural remedy and highlights its importance beyond culinary applications. Whether you’re looking to enhance the flavor of your meals or improve your health, incorporating tamarind into your diet can offer both delicious tastes and therapeutic benefits.
Varieties of Tamarind and Their Culinary Uses

Tamarind is not a one-size-fits-all ingredient; its varieties significantly influence the culinary landscape of Asian cuisine. For instance, Sweet Tamarind is often used in Thai dishes, where its balanced sweetness enhances desserts and snacks without overpowering them. On the other hand, Sour Tamarind is a staple in Indian cooking, providing a robust tang that is essential in savory dishes such as chutneys and curries. Each variety brings its unique flavor profile to the table, making tamarind a versatile and indispensable ingredient in Asian kitchens.
Beyond these common types, there are specialized forms of tamarind that cater to specific culinary needs. Seedless Tamarind, for example, is prized for its convenience, eliminating the hassle of deseeding, which is particularly useful in fast-paced cooking environments. Compressed Tamarind is another form, typically used to make tamarind paste, a concentrated flavor booster in many Asian recipes. Whether it’s adding a tangy punch to marinades or a subtle tartness to beverages, the different types of tamarind ensure that chefs can achieve the perfect flavor balance in their dishes.
Discover Tamarind Asian Cuisine with Indulge’s Culinary Tours
INDULGE offers an exclusive opportunity to dive deep into the world of Asian flavors, including the unique taste of tamarind, through their specialized culinary tours in Zurich. These tours are designed to provide a hands-on experience with authentic Asian cuisine, where tamarind plays a starring role in many dishes. Participants will have the chance to taste tamarind in various forms:
- As a key ingredient in sauces and marinades
- In traditional beverages
- Through innovative dishes curated by local chefs
By joining an INDULGE culinary tour, participants not only relish the flavors but also gain insights into the culinary techniques and cultural significance of tamarind in Asian cooking. This immersive experience is perfect for food enthusiasts eager to expand their palate and knowledge. Each tour is guided by experts who share stories and secrets behind the recipes, making every dish more enjoyable. Ready to explore the tangy and sweet world of tamarind? Book your culinary adventure with INDULGE today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is tamarind used in Asian cooking?
Yes, tamarind is widely used in Asian cooking. It is a versatile ingredient that enhances flavors in sauces, soups, marinades, and beverages, providing a unique sour taste that is essential in many traditional Asian dishes.
Which cuisine is tamarind used in?
Tamarind is used in various Asian cuisines, including Thai and Indian. It plays a significant role in creating the distinctive sweet and sour flavors found in many traditional dishes such as curries, chutneys, and sauces.
Is tamarind Asian or Mexican?
Tamarind originally comes from Africa but has become heavily integrated into Asian cuisines. It is also used in other regions, including Latin America, but it has a profound connection and historical significance in Asia, particularly in India and Thailand.
Where is tamarind most popular?
Tamarind is most popular in Asia, especially in India and Thailand, where it has a deep-rooted historical significance and is heavily integrated into the local cuisines. It is used in a variety of dishes, from sauces and marinades to traditional medicines and beverages.